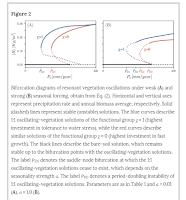
The predictions for a warmer and drier climate and for increased likelihood of climate extremes raise high concerns about the possible collapse of dryland ecosystems, and about the formation of new drylands where native species are less tolerant to water stress. Using a dryland-vegetation model for plant species that display different tradeoffs between fast growth and tolerance to droughts, Omer Tzuk et al., found that ecosystems subjected to strong seasonal variability, typical for drylands, exhibited a temporal period-doubling route to chaos that results in early collapse to bare soil. They further found that fast-growing plants go through period doubling sooner and span wider chaotic ranges than stress-tolerant plants. They propose the detection of period-doubling signatures in power spectra as early indicators of ecosystem collapse that outperform existing indicators in their ability to warn against climate extremes and capture the heightened vulnerability of newly-formed drylands. The proposed indicator is expected to apply to other types of ecosystems, such as consumer–resource and predator–prey systems. Thus, they conclude by delineating the conditions ecosystems should meet in order for the proposed indicator to apply.








No comments:
Post a Comment